Better Tools for Fast and Convenient Patulin Analysis
Analytical Standards and SupelMIP® SPE Cartridges

The mycotoxin patulin is often found in rotten apples. It is mostly produced by Aspergillus, Penicillium and Byssochlamys and shows a variety of short-term and long-term effects in animal studies, ranging from gastrointestinal problems and neurotoxicity to genotoxicity and teratogenicity. Therefore, many countries set limits for patulin content in apple products. For a precise detection of patulin, we offer SPE cartridges for purification and a comprehensive range of analytical standards.
Extraction of Patulin with Molecular Imprinted Polymer
Historically, analytical methods for patulin have employed liquid-liquid extraction (LLE) followed by HPLC separation with UV detection at 276 nm. Researchers have highlighted problems with these methodologies, including:
- Tedious sample preparation associated with liquid-liquid extraction
- Patulin instability in alkaline conditions resulting from sodium carbonate cleanup
- The requirement of extra cleanup or chromatographic method development to prevent the coelution of patulin and interfering matrix component 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF)[1,6]
Therefore, a quick, simple and robust sample preparation method for patulin analysis is needed. To propose an accurate solution, Supelco has developed a method based on the technology of molecularly imprinted polymers. These SupelMIP® SPE Patulin extraction cartridges selectively clean and concentrate patulin prior to analysis by HPLC.
The process to extract patulin from apple juice is described below.
SPE Procedure for Patulin Extraction and Cleanup
- Dilute apple juice in a 1:1 ratio with 2% acetic acid.
- At a drop rate of 1–2 drops per second, condition the cartridge with 2 mL of acetonitrile and 1 mL de-ionized water.
- Load 4 mL of the pre-treated sample into the cartridge.
- At a flow rate of 0.5–1 mL/minute, wash with 1 mL 1% sodium bicarbonate solution and 2 mL de-ionized water. Apply a strong vacuum (–0.8 bar or -20" of in Hg) for 10 seconds after the wash steps to dry the SPE tube.
- Pulling a strong vacuum, elute the analyte with 0.5 mL diethyl ether and 2 mL ethyl acetate.
- Evaporate the eluted samples to dryness, and reconstitute in 1 mL of 0.1% acetic acid in water
This MIP-phase SPE procedure yielded high analyte recovery with excellent reproducibility. The average recovery of patulin was calculated to be 84% with a relative standard deviation (RSD) of 2%. As seen in Figure 1, chromatographic analysis showed that no direct interferences with patulin detection were observed. Unlike LLE procedures, the clean-up procedure using SupelMIP® SPE Patulin successfully removed HMF and other common interfering components from the final extract. As a result, patulin was easily detectable in apple juice at concentrations of 50 ng/mL.
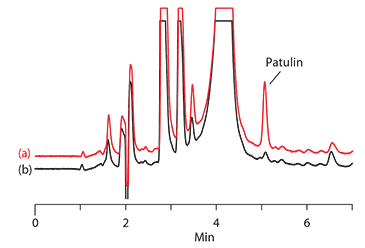
Figure 1.Chromatogram of apple juice after SPE clean-up
(a) spiked at 50 ng/mL with patulin and
(b) with no patulin spike.
HPLC Conditions
Column: Ascentis® Express C18, 15 cm x 2.1 mm, 2.7 µm particles (53825-U); Mobile Phase: (A) 95:5 water:acetonitrile; (B) 100% acetonitrile; Gradient: Hold at 100% A for 6 min; 0% to 80% B in 0.1 min; hold at 80% B for 3 min, 80% to 0% B in 0.1 min, hold at 100% A for 13 min; Flow Rate: 0.2 mL/min.; Column Temp.: 30 °C; Detector: UV (276 nm); Injection: 10 µL
Analytical Standards for Mycotoxin Analysis
For precise quality control of patulin in food and feed, we provide our customers with analytical neat standards and standard solutions. We also offer a stable, non- radioactive fully 13C–isotopically labeled version of patulin, with the same physiochemical and chromatographic behaviors (Figure 2). This internal standard accounts for variations during sample preparation, clean-up and ionization.

Figure 2.Molecular Structure of Patulin
Legal Information
SupelMIP and Ascentis are registered trademarks of Sigma-Aldrich Co. LLC.
如要继续阅读,请登录或创建帐户。
暂无帐户?