Purification or Removal of Biotin and Biotinylated Substances
Streptavidin Sepharose High Performance
Biotin and biotinylated substances bind to streptavidin, a molecule isolated from Streptomyces avidinii. The binding of streptavidin to biotin is one of the strongest known noncovalent biological interactions. Hence, denaturing conditions are generally required for the efficient elution of biotinylated biomolecules. Alternatively, biotinylated biomolecules bound to streptavidin chromatography media can be used to capture interacting target substances such as proteins. Impurities are removed by washing, and the enriched target protein is eluted using relatively mild elution conditions.
Chromatography medium characteristics
Characteristics of Streptavidin Sepharose High Performance AC medium are given in Table 3.5
1Short term refers to the pH interval for regeneration, cleaning-in-place, and sanitization procedures. The long term refers to the pH interval over which the medium is stable over a long period of time without adverse effects on its subsequent chromatographic performance.
Purification options
Streptavidin Sepharose High Performance is available in chromatography media packs and is prepacked in HiTrap® 1 mL columns, MultiTrap™ 96-well plates, and SpinTrap™ minicolumns (Table 3.6). These different formats can be used for protein purification and enrichment, where a biotinylated antibody (or other biotinylated molecule) is attached to the Streptavidin and the protein of interest is enriched through the affinity interaction with the antibody/target molecule.
Streptavidin Mag Sepharose magnetic beads are also available for small-scale immunoprecipitation and purification of biotinylated molecules.
1 See Appendix 4 to convert flow velocity (cm/h) to volumetric flow rate (mL/min). The maximum operating flow is calculated from measurement in a packed column with a bed height of 10 cm and i.d. of 5 cm.
Purification example
An alternative to labeling the biomolecule, for example the antibody, with biotin is to use 2-iminobiotin that binds to streptavidin above pH 9.5 and can be eluted at pH 4.0 (Figure 3.5).
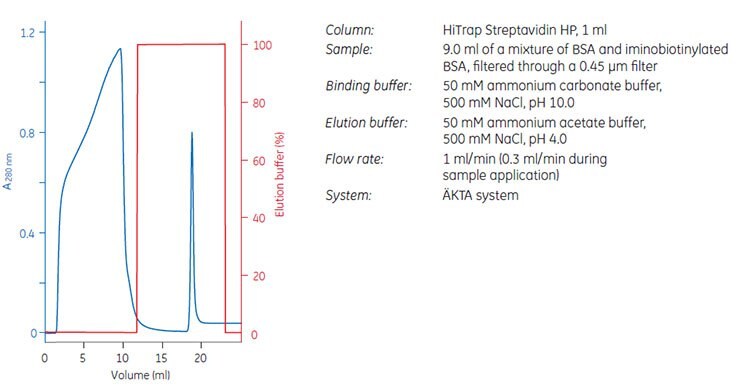
Figure 3.5. Purification of iminobiotinylated BSA on HiTrap® Streptavidin HP, 1 mL.
Enrichment of a particular protein is often desired to increase its signal in subsequent analysis steps. In this example Streptavidin HP SpinTrap™ was used for enrichment of human transferrin from E. coli sample. The concentration of the protein of interest was 0.15% of the total E. coli protein content, which approximately corresponds to the concentration of a medium-abundance protein. Capture of transferrin was achieved using a biotinylated antibody (polyclonal rabbit antihuman transferrin immobilized on the medium).
Analysis by SDS-PAGE of the collected fractions from the runs revealed a significant enrichment of transferrin (Figure 3.6). Recovery of the start material was 60% to 70% with the majority of the protein eluted in the first elution step. The enrichment of transferrin relative to the start material was approximately 100-fold with Streptavidin HP SpinTrap™.
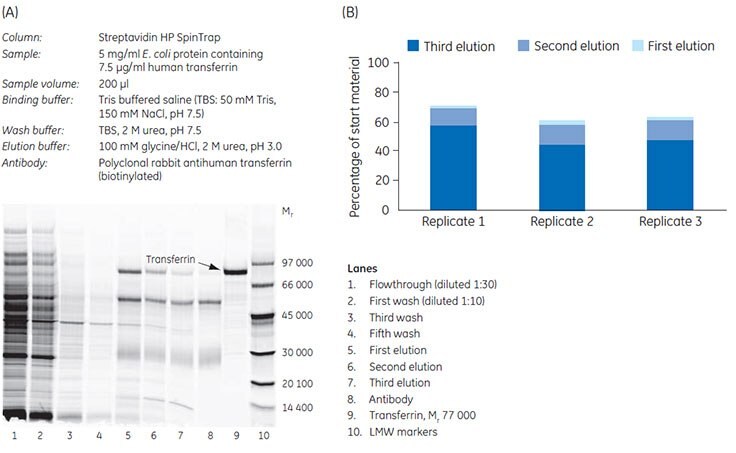
Figure 3.6. Enrichment of transferrin from E. coli cell lysate. (A) Analysis by SDS-PAGE (wash steps 2 and 4 have been omitted from the gel). The gel was post-stained with Deep Purple Total Protein Stain and scanned. (B) All three elution steps were analyzed using ImageQuant™ TL software. Recovery (percentage of start material) of three replicates is shown.
Performing a separation
HiTrap® Streptavidin HP
The following protocol describes AC using a HiTrap® Streptavidin HP 1 mL column by syringe, using a pump, or a chromatography system.
- Equilibrate the column with 10 CV of binding buffer.
- Apply the sample. For optimal results, use a low flow rate of 0.1 to 0.5 mL/min during sample application.
- Wash with at least 10 CV of binding buffer or until no material appears in the eluent (monitored by UV absorption at A280 nM).
- Elute with 10 to 20 CV of elution buffer.1
1 Since elution conditions can be quite harsh, collect fractions into neutralization buffer (100 to 200 µL 1 M Tris-HCl, pH 9.0 per mL of fraction), so that the final pH of the fractions will be approximately neutral or perform a rapid buffer exchange on a desalting column (see Buffer exchange and desalting, Appendix 1).
The harsh conditions required to break the streptavidin-biotin bond can affect both the sample and the ligand. Streptavidin Sepharose columns cannot be reused after elution under these conditions.
Antigen purification
Antigens can be purified from biotinylated biomolecule (often antibody)-antigen complexes bound to streptavidin. The following method is adapted for HiTrap® Streptavidin HP.
- Solubilize the antigen with an appropriate amount of solubilization buffer, clear the sample by centrifuging at 12 000 × g for 15 min.
- SAdd the biotinylated antibody and adjust the volume to 1 mL.
- SIncubate with end-over-end mixing, for at least 1 h or overnight.
- SEquilibrate the column with 10 CV of solubilization buffer.
- SApply antibody-antigen solution to the column at a low flow rate such as 0.2 mL/min. If the sample volume is less than 1 mL, apply the sample, and leave for a few minutes to allow binding to take place.
- SWash out unbound sample with 10 CV of solubilization buffer or until no material is found in eluent (monitored by UV absorption at A280 nM).
- SElute with 5 to 10 CV of elution buffer1.
1 Since elution conditions are quite harsh, it is recommended to collect fractions into neutralization buffer (100 to 200 µL of 1 M Tris-HCl, pH 9.0 per ml of fraction), so that the final pH of the fractions will be approximately neutral or perform a rapid buffer exchange on a desalting column (see Buffer exchange and desalting, Appendix 1).
Streptavidin HP MultiTrap™ Materials 96-well plate
The protocol is designed for enrichment of target proteins by using immobilized antibodies. Centrifuge the MultiTrap™ 96-well plates at 700 × g or use vacuum. If vacuum is used, apply -0.15 bar until the wells are empty, then slowly increase the vacuum to -0.3 bar (do not apply more vacuum than -0.5 bar). Turn off the vacuum after approximately 5 s.
Mix briefly before removal of liquid in the equilibration, wash, and elution steps to increase the efficiency of the step. Incubating on a plate shaker is recommended. Remember to change or empty the collection plate between steps.
1. Remove storage solution
A. Suspend the medium by gently shaking the plate upside down.
B. Remove top and bottom seals and place plate on the collection plate.
C. Remove the storage solution by centrifugation for 1 min at 700 × g.
2. Equilibration for immobilization (perform this step three times)
A. Add 400 µL binding buffer per well, mix briefly and centrifuge for 1 min at 700 × g to equilibrate the medium.
3. Binding of biotinylated antibody
A. Immediately after equilibration, add 200 µL of the biotinylated antibody solution per well (0.1 to 1.0 mg/mL in binding buffer).
B. Incubate on shaker for 20 min.
C. Centrifuge for 1 min at 700 × g to remove unbound antibody.
4. Blocking (perform this step twice)
A. Add 400 µL blocking buffer per well and incubate on shaker for 5 min to block free biotin binding sites.
B. Centrifuge for 1 min at 700 × g.
5. Washing (perform this step three times)
A. Add 400 µL binding buffer per well and mix briefly.
B. Centrifuge for 1 min at 700 × g.
6. Binding of target protein
A. Add 200 µL clarified sample in binding buffer per well and incubate on shaker for 60 min.
B. Centrifuge for 1 min at 700 × g to wash out unbound protein. Collect flowthrough.
7. Washing
A. Add 400 µL binding/wash buffer per well and mix briefly.
B. Centrifuge for 1 min at 700 × g. Perform this step five times in total. (Collect and save washes in case troubleshooting is needed).
8. Elution (perform this step three times)
A. Add 200 µL of desired elution buffer and shake for 1 min.
B. Centrifuge for 1 min at 700 × g.
C. Collect the eluates in separate collection plates.
Streptavidin HP SpinTrap™ columns
This protocol is designed for enrichment of target proteins by using immobilized antibodies. In each step, place the SpinTrap™ column in a fresh 2 mL microcentrifuge tube for liquid collection. Lids and bottom caps of Streptavidin HP SpinTrap™ are used during the incubation and elution but not during equilibration and washing. Before centrifugation, remove the bottom cap and slightly open the screw cap lid (twist the cap lid ~ 90º counterclockwise).
1. Remove storage solution
A. Break off the bottom cap from the spin column. Save the bottom cap.
B. Remove the storage solution by centrifugation for 1 min at 150 × g.
2. Equilibrate for immobilization (perform this step three times)
A. Add 400 μL binding buffer and centrifuge for1 min at 150 × g to equilibrate the medium.
B. Remove the binding buffer.
3. Binding biotinylated antibody
A. Immediately after the equilibration, add 200 μL of the biotinylated antibody 0.1 to 1.0 mg/mL).
B. Fully suspend the medium by manual inversion and incubate with slow, end-over-end mixing for 20 min at room temperature.
C. Centrifuge for 1 min at 150 × g to remove unbound antibody.
4. Blocking (perform this step twice)
A. Add 400 μL blocking buffer.
B. Mix by manual inversion and incubate with end-over-end mixing for 5 min to block free biotin binding sites.
C. Centrifuge for 1 min at 150 × g.
5. Washing (perform this step three times)
A. Add 400 μL binding buffer and centrifuge for 1 min at 150 × g.
6. Binding of target protein
A. Add 200 μL clarified sample in binding buffer.
B. Mix by manual inversion and incubate with slow, end-over-end mixing for 60 min at room temperature.
C. Centrifuge for 1 min at 150 × g to wash out unbound protein. Collect flowthrough.
7. Washing (perform this step five times)
A. Add 400 μL wash buffer and centrifuge for 1 min at 150 × g.
B. During optimization/troubleshooting: Collect flowthrough.
8. Elution (perform this step three times)
A. Add 200 μL of desired elution buffer and mix by inversion.
B. Centrifuge for 1 min at 1000 × g.
C. Collect the eluates in individual tubes.
Storage
Wash chromatography media and HiTrap® columns with 20% ethanol (use approximately 5 CV for packed media) and store at 4 °C to 8 °C. Streptavidin MultiTrap™ and Streptavidin SpinTrap™ are for single-use only.
如要继续阅读,请登录或创建帐户。
暂无帐户?