Application Note - Sterility Testing of Products to be Diluted in Isopropyl Myristate
Sterility testing of viscous oils, water-in-oil emulsions and fatty base ointments
Membrane filtration is the Pharmacopoeia method of choice for sterility testing. Viscous products, such as creams and ointments, can be difficult to filter and are normally diluted in a sterile solvent, such as Isopropyl Myristate (IPM). Testing such products may be problematic if specific testing procedures are not implemented and appropriate devices are not used. The Steritest™ NEO device, TZHVSL210, is the perfect choice for testing solvents, creams, ointments and veterinary injectables due to the solvent-resistant nylon canister, Durapore® (PVDF) membrane, reinforced base structure and canister connection.

Materials
- Green base Steritest™ NEO filtration device: TZHVSL210
- Isopropyl Myristate (IPM) sterile, ready to use: 1.46628.0006
- Soybean–Casein Digest medium (SCDB), Fluid Thioglycollate Medium (FTM), Clear Fluid Thioglycollate Medium (CTM), Rinsing Fluid A, Fluid K: double packaged media and fluids available; different formats available. Culture media and rinsing fluids
Equipment
Steritest™ Symbio Pump: for Laminar Flow Hood or Isolator.
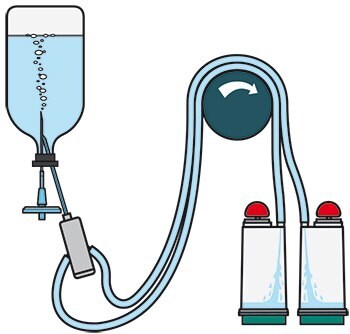
Sterility Testing Method and Sample Preparation
- Set up the Steritest™ Pump and device system. Use Steritest™ NEO device TZHVSL210.
- Warm IPM and Fluid K bottles to a maximum of 44 °C.
- Take one 100 mL bottle of warm IPM. Wipe the bottle with 70% IPA before placing it in the testing environment.
- Aseptically dispense the appropriate amount of product as required by the USP/EP/JP into the bottle of warm IPM.
Test Method
- Take the other bottles, one at a time, wiping each bottle before placing it in the testing environment.
- Pre-wet each membrane with 50 mL of warm IPM.
- Filter the diluted product.
- Rinse each membrane three times with 100 mL of warmed Fluid K (600 mL total per Steritest™ NEO unit).
Fill each canister with 100 mL Fluid K and then filter the fluid. When approximately 30 to 50 mL of Fluid K have passed through the membrane, gently swirl the canister to rinse residuals of IPM from the canister sides. - Then allow all the Fluid K to filter through the membrane. Repeat this procedure two additional times with Fluid K.
- Do a last rinse with 100 mL of Fluid A per membrane to remove residuals of Fluid K.
- Add growth media Soybean–Casein Digest medium (SCDB) and Clear Fluid Thioglycollate Medium (CTM) to each respective canisters and start incubation (SCDB at 20 to 25 °C for 14 days; FTM at 30 to 35 °C for 14 days).
- Observe for growth/no growth.
Note: In our experiments, poor rinsing was observed when the membrane filter was covered with liquid throughout the filtration steps. To avoid this, the entire volume of test article was allowed to filter through the Steritest™ NEO devices, followed by the entire volume (of each) Fluid K rinse.
Pharmacopoeia Acceptance Criteria and Method Suitability Test
According to Pharmacopoeias, method suitability must be tested for proper recovery. Inoculate the last Fluid rinse with not more than 100 CFU with the microorganisms recommended in the Pharmacopoeias. Environmental isolates can also be tested. When the filtration is complete, add media (SCDB and FTM) to the canisters and incubate for the proper time and temperature, following Pharmacopoeia recommendations. Then observe the canisters and see if growth Pharmacopoeia acceptance criteria are met.
Note: In case of direct inoculation of microorganisms into IPM, addition of 9% of NaCl Peptone buffer ensures recovery rate above 50%.
Further Reading and Information
如要继续阅读,请登录或创建帐户。
暂无帐户?