(ELISA) Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Typically performed in multi-well microtiter plates, ELISAs are a molecular biology assay commonly used for the detection and quantification of diverse molecules, including peptides, proteins, and antibodies. Such assays can detect molecules of interest at the pg/mL level and are critical for both basic research and disease research application needs.
ELISA Assays: Antibody-Antigen Interactions
The fundamental molecular components of an ELISA typically include the use of antibody conjugated to an enzyme, an immobilized molecule(s) of interest, and a detection substrate. A critical aspect that determines the success and quality of data obtained from an ELISA is dependent on the affinity and specificity of antibody-antigen interactions. Antigen-antibody interactions are influenced by numerous factors, including pH, temperature, and ionic strength.
ELISA Detection Formats
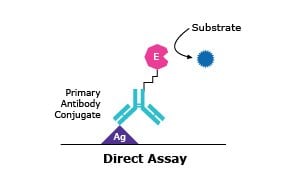
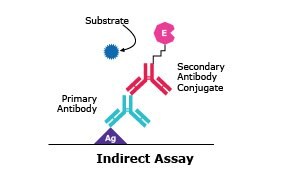
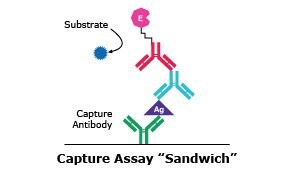
ELISAs that use direct detection methods require an immobilized antigen that is bound directly to the surface of an assay plate or indirectly by a capture antibody, followed by an antigen-specific primary antibody conjugated to an enzyme, and the detection substrate. The more commonly used indirect detection format incorporates both an unconjugated primary antibody, followed by a conjugated secondary antibody that is specific to the detection of the primary antibody. Indirect detection benefits from increased immunoreactivity with the target antigen as the conjugated enzyme element is only present on the secondary antibody. In addition to direct and indirect detection methods, capture or “sandwich” assays use an additional antigen-capturing antibody that is first attached to the microplate surface, followed by the use of both a primary and an enzyme-conjugated secondary antibody, similar to the indirect method previously described.
Related Technical Articles
- Conferma™ Sandwich ELISAs are created with a focus on their critical components. Combined with finished kit quality control analysis, explore Conferma™ ELISA validation that provides a high degree of consistency with each lot to give you confidence in your research.
- The inherent immune ability of an animal can be leveraged to generate antibodies that bind to specific molecules.
- The enzyme-linked immunosorbent spot (ELISpot ) assay enables visualization of multiple secretory products from a single responding cell. The ELISpot provides both qualitative (type of immune protein) and quantitative (number of responding cells) information.
- Troubleshoot and optimize ELISAs using this guide that includes solutions to some of the most common sources of problems for assay development.
- Accelerate your time to market with fit-for-use products which offer the quality, consistency, and documentation necessary for every step of your IVD development and manufacturing needs.
- See All
Related Protocols
- This article offers 4 popular ELISA protocols: Sandwich ELISA protocol, Phosphorylation Assay Procedure, EIA Assay Procedure, & Cell-based Assay Procedure.
- ELISA protocols providing detailed instructions on performing indirect ELISA and Capture ELISA . Learn more about recommended products and techniques for performing both sandwich ELISA and indirect ELISA experiments.
- Cell Proliferation ELISA, BrdU (colorimetric) Protocol & Troubleshooting
- Measure and compare the activity of proteases with this non-specific protease activity assay using casein. Use this assay as a standardized procedure to determine the activity of proteases for quality control.
- cAMP measurements are obtained using an ELISA assay (Harlow and Lane 1988). Commercial radio-immunoassays, or ELISA kits, to assay cAMP can be purchased from various manufacturers.
- See All
To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?