Desalting/Buffer Exchange and Concentration for Affinity Chromatography of Tagged Proteins
Extracted from Affinity Chromatography Vol. 2: Tagged Proteins, GE Healthcare, 2016
Desalting at laboratory scale is a well-proven, simple, and very fast method that will rapidly remove low molecular weight contaminants at the same time as transferring the sample into the desired buffer in a single step.
GE offers a range of prepacked chromatography columns and 96-well filter plates that can be used manually, together with a chromatography system, or in high-throughput applications (Table 11.1). The majority of these products contain Sephadex G-25, an SEC medium that allows effective removal of low molecular weight substances from proteins with Mr > 5000. PD MiniTrap™ G-10 and PD MidiTrap™ G-10 columns contain Sephadex G-10. These prepacked, single-use gravity columns allow desalting/buffer exchange of smaller proteins with Mr > 700.
Use desalting/buffer exchange when needed, before purification, between purification steps, and/or after purification. These are very fast methods compared with dialysis, but remember that each extra step can reduce yield and that desalting dilutes the sample (centrifugation protocols do not dilute samples).
Use Sephadex G-25 products to remove salts and other low molecular weight compounds from proteins with Mr > 5000 and Sephadex G-10 products for proteins (peptides) with Mr > 700.
Occasionally, purified fractions may have a concentration of target protein that is too low, and sample concentration is needed. Vivaspin® sample concentrators, which perform gentle, nondenaturing membrane ultrafiltration, are suitable for this purpose. See later in this chapter for a discussion of Vivaspin® products.
Desalting provides several advantages over dialysis. Dialysis is generally a slow technique that requires large volumes of buffer and carries the risk that material and target protein activity will be lost during handling. When desalting, sample volumes of up to 30% of the total volume of the desalting column can be processed. The high speed and capacity of the separation allows even relatively large sample volumes to be processed rapidly and efficiently in the laboratory. Sample concentration does not influence the separation as long as the concentration of proteins does not exceed approximately 70 mg/mL when using normal aqueous buffers, and provided that the target protein is stable and soluble at the concentration used. Use 100 mM ammonium acetate or 100 mM ammonium hydrogen carbonate if volatile buffers are required.
Consider whether the conditions of the sample can be adjusted simply by additions or dilution of the sample. For affinity chromatography (AC) or ion exchange chromatography (IEX), it may be sufficient to adjust the pH of the sample and, if necessary, the ionic strength of the sample. Before hydrophobic interaction chromatography (HIC) ammonium sulfate is normally added and the pH is adjusted.
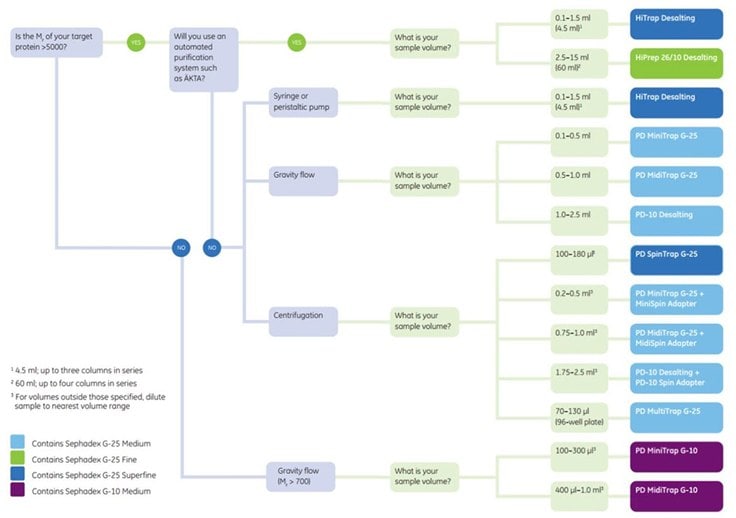
Figure 11.1.Selection guide: Prepacked columns for desalting/buffer exchange.
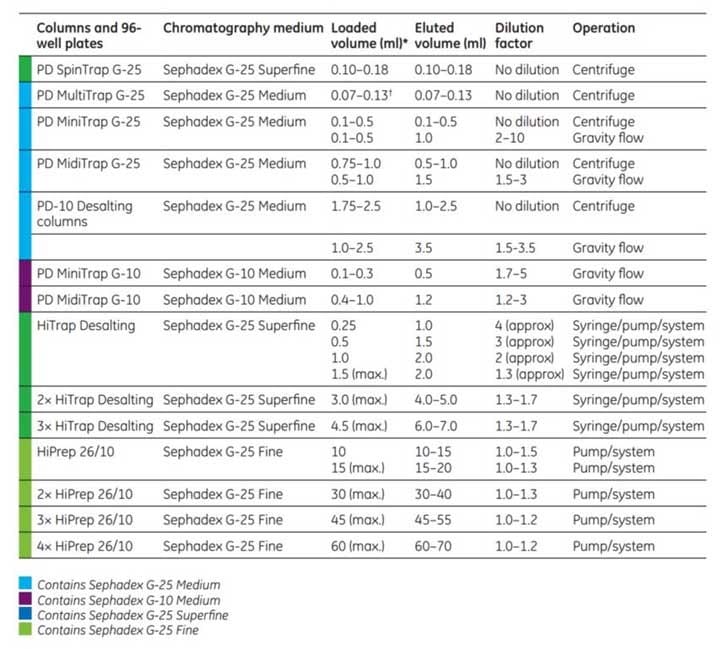
Table 11.1.Selection table for desalting/buffer exchange columns
* For sample volumes less than 0.14 mL is recommended to apply a stacker volume of equilibration buffer to reach a total of 0.14 mL after the sample has fully absorbed.
† For sample volumes less than 0.10 mL it is recommended to apply a stacker volume of equilibration buffer to reach a total of 0.10 mL after the sample has fully absorbed.
General Considerations
Small-scale Desalting of Samples
For sample volumes ranging from 0.1 to 2.5 mL, it is possible to run multiple samples in parallel with PD-10 Desalting, PD MidiTrap™ G-25, and PD MiniTrap™ G-25 columns. Two different protocols are available for these columns: one for manual use on the laboratory bench and one for use together with a standard centrifuge in combination with a Spin Adapter. For smaller proteins (peptides) (Mr > 700), PD MiniTrap™ G-10 and PD MidiTrap™ G-10 columns may be used.
For smaller sample volumes, multiple samples can be run on PD SpinTrap™ G-25 spin columns together with a microcentrifuge or PD MultiTrap™ G-25 96-well plate using centrifugation for extraction (Figure 11.2 A-D). Although possible to perform, using PD MultiTrap™ G-25 with vacuum is not recommended.

Figure 11.2.(A) PD SpinTrap™ G-25 sample preparation. (B) PD MultiTrap™ G-25. (C and D) Spin Adapters are used together with PD-10 Desalting columns, PD MidiTrap™ G-25, and PD MiniTrap™ G-25 to enable use in a standard centrifuge.
Desalting Larger Sample Volumes Using HiTrap® and HiPrep™ Columns
Connect up to three HiTrap® Desalting columns in series to increase the sample volume capacity. For example, two columns allow a sample volume of 3 mL, and three columns allow a sample volume of 4.5 mL (Table 11.1).
Connect up to four HiPrep™ 26/10 Desalting columns in series to increase the sample volume capacity. For example, two columns allow a sample volume of 30 mL, and four columns allow a sample volume of 60 mL. Even with four columns in series, the sample can be processed in 20 to 30 min with no problems due to back pressure.
Buffer Preparation
All commonly used aqueous buffers can be used for desalting/buffer exchange. Often a buffer with 25 to 50 mM concentration of the buffering substance is sufficient. A salt concentration of at least 25 mM is recommended to prevent possible ionic interactions with the chromatography medium. Sodium chloride is often used for this purpose. At salt concentrations above 1 M, hydrophobic substances may be retarded or may bind to the chromatography medium. At even higher salt concentrations (> 1.5 M ammonium sulfate), the column packing shrinks.
Sample Preparation
Sample concentration does not influence the separation as long as the viscosity does not differ by more than a factor of 1.5 from that of the buffer used. This corresponds to a maximum concentration of 70 mg/mL for proteins, when normal, aqueous buffers are used.
The sample should be fully solubilized. Centrifuge or filter (0.45 µm filter) immediately before loading to remove particulate material if necessary.
Buffer Exchange
Protein solubility often depends on pH and/or ionic strength (salt concentration), and the exchange of buffer may therefore result in precipitation of the protein. Also, protein activity can be lost if the change of pH takes it outside of the range where the protein is active. Samples that have been obtained after purification will usually be free from particles, unless the purified protein or a contaminant has been aggregated.
The protocols in the following sections describe desalting and buffer exchange using different formats of prepacked columns.
Small-scale Desalting and Buffer Exchange with PD Desalting columns
PD-10 Desalting columns, PD MidiTrap™ G-25, PD MiniTrap™ G-25, PD SpinTrap™ G-25, and PD MultiTrap™ G-25 columns and 96-well filter plates are prepacked with Sephadex G-25 for group separation of high (Mr > 5000) from low molecular weight substances (Mr < 1000) by desalting and buffer exchange. PD MiniTrap™ G-10 and PD MidiTrap™ G-10 columns contain Sephadex G-10. These prepacked, single-use gravity columns allow desalting/buffer exchange of smaller proteins with Mr > 700. This collection of columns and plates covers the sample volume range from 70 µL to 2.5 mL and supports processing multiple samples in parallel.
PD SpinTrap™ G-25
Figure 11.3.PD SpinTrap™ G-25 columns are single-use columns for rapid desalting and buffer exchange of biomolecules with Mr > 5000.
PD SpinTrap™ G-25 is a single-use spin column that is designed for rapid, highly reproducible desalting and buffer exchange of 100 to 180 µL samples using a standard microcentrifuge (Figure 11.2 A and 11.3). The columns provide highly reproducible, parallel desalting/buffer exchange and cleanup of protein samples without sample dilution. The spin columns are prepacked with Sephadex G-25 Superfine, an SEC medium that allows effective removal of low molecular weight substances from biomolecules with Mr > 5000.
Each pack of PD SpinTrap™ G-25 contains prepacked columns and collection tubes for 50 preparations.
Buffer
Equilibration buffer: Buffer of choice
Desalting procedure
- Suspend the chromatography medium by vortexing. Loosen screw cap lid and remove bottom closure using the plastic bottom cap removal tool.
- Place the column in an appropriately sized collection tube and remove the storage solution by centrifugation for 1 min at 800 × g.
- Equilibrate by adding 400 µL of equilibration buffer and centrifuge for 1 min at 800 × g. Discard the flowthrough and replace the collection tube. Repeat this procedure four more times.
To ensure optimal results, it is critical to equilibrate the spin column with a total of 2 mL of equilibration buffer to completely remove the storage solution.
- Replace the used collection tube with a new clean collection tube for sample collection.
- Apply 100 to 180 µL of sample slowly to the middle of the prepacked column.
- Elute by centrifugation at 800 × g for 2 min.
Recovery is dependent on type of protein or other biomolecule. Typically, recovery is in the range of 70% to 90%. Concentration of the sample (e.g., using a Vivaspin® sample concentrator) can improve recovery. For sample volumes less than 140 µL it is recommended to add equilibration buffer to reach a total volume of 140 µL after the sample has fully absorbed into the column bed.
For desalting larger sample volumes, use larger-scale PD cleanup and desalting products or HiTrap® and HiPrep™ columns; see Table 11.1. For desalting of multiple samples, use PD MultiTrap™ G-25.
PD MultiTrap™ G-25

Figure 11.4.PD MultiTrap™ G-25 96-well plates offer rapid, highly reproducible cleanup of biomolecules with Mr > 5000.
PD MultiTrap™ G-25 96-well plates are designed for high-throughput desalting, buffer exchange, and cleanup of proteins, with high reproducibility well-to-well and plate-to-plate (Figure 11.4). Using the 96-well plates, multiple samples can be run conveniently and reproducibly in parallel (Figure 11.5). PD MultiTrap™ G-25 can be operated manually or in automated mode using a robotic system equipped with a centrifugation device to desalt or buffer exchange sample volumes ranging from 70 to 130 µL. For sample volumes less than 100 µL it is recommended to apply a stacker volume of equilibration buffer to reach a total of 100 µL after the sample has fully absorbed. Elution can be performed by centrifugation. Although possible to perform, using PD MultiTrap™ G-25 with vacuum is not recommended due to reduced reproducibility compared with operation using centrifugation.
The wells are prepacked with Sephadex G-25 Medium, an SEC medium that allows effective removal of low molecular weight substances from biomolecules with Mr > 5000.
Each pack of PD MultiTrap™ G-25 contains four prepacked 96-well plates, allowing desalting or buffer exchange of up to 384 samples.
Convenient collection plates (five per pack) are available separately.
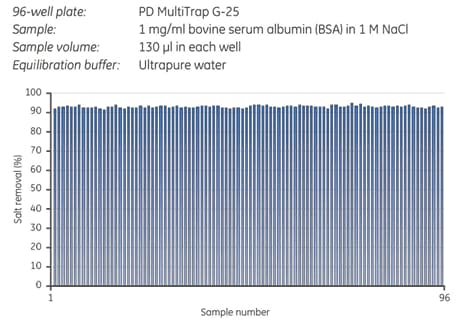
Figure 11.5.Removal of NaCl from BSA on a PD MultiTrap™ G-25 96-well plate showed highly reproducible results. The average desalting capacity was 93% and the well-to-well variation was 1% (relative standard deviation).
Centrifugation Protocol
Buffer
Equilibration buffer: Buffer of choice
Desalting procedure
- Suspend the chromatography medium by gently shaking the plate upside down. Remove top and bottom seals and place plate on the collection plate.
- Remove the storage solution by centrifugation for 1 min at 800 × g.
- Equilibrate by adding 300 µL of equilibration buffer and centrifuge for 1 min at 800 x g. Discard the flowthrough and replace the collection tube. Repeat this procedure four more times.
To ensure optimal results, it is critical to equilibrate each well with a total of 1.5 mL of equilibration buffer to completely remove the storage solution.
- Replace the used collection plate with a new, clean collection plate for sample collection.
- Apply 70 to 130 µL of sample to the middle of the prepacked wells.
- Elute by centrifugation at 800 × g for 2 min.
Recovery is dependent on type of protein or other biomolecule. Typically, the recovery is in the range of 70% to 90%. Concentration of the sample (e.g., using a Vivaspin® sample concentrator) can improve recovery. For sample volumes less than 100 µL it is recommended to add equilibration buffer to reach a total volume of 100 µL after the sample has fully absorbed into the column bed.
For desalting larger sample volumes, use larger-scale PD cleanup and desalting products or HiTrap® and HiPrep™ columns; see Table 11.1.
PD MiniTrap™ G-25 and PD MidiTrap™ G-25

Figure 11.6.PD MiniTrap™ G-25 prepacked columns for cleanup of proteins with Mr > 5000 in sample volumes up to 500 µL (PD MiniTrap™ G-25; left) and 1.0 mL (PD MidiTrap™ G-25; right).
PD MiniTrap™ G-25 and PD MidiTrap™ G-25 are designed for convenient desalting and buffer exchange of 100 to 500 µL (PD MiniTrap G-25) and 0.5 to 1.0 mL (PD MidiTrap™ G-25) volume of protein sample (Figure 11.6). The columns are prepacked with Sephadex G-25 Medium, an SEC medium that allows effective removal of low molecular weight substances from proteins with Mr > 5000. These columns provide an excellent alternative to PD SpinTrap™ G-25 columns because of the increased sample volume capacity.
For increased flexibility, the products have two alternative application protocols, using either gravity or centrifugation. The gravity protocol allows simple cleanup of multiple samples in parallel without the need for a purification system. With the centrifugation protocol, samples are run in a standard centrifuge with minimal dilution of the eluted sample.
Each pack of PD MiniTrap™ G-25 and PD MidiTrap™ G-25 contains 50 prepacked columns and four adapters that are required when using the centrifugation protocol.
Gravity protocol
Buffer
Equilibration buffer: Buffer of choice
Desalting Procedure
- Remove the top cap and pour off the column storage solution. Remove the bottom cap.
- Fill the column with equilibration buffer and allow the equilibration buffer to enter the packed bed completely. Repeat twice and discard the flowthrough.
To ensure optimal results, it is critical to equilibrate the column with a total of 8 mL (PD MiniTrap™ G-25) or 15 mL (PD MidiTrap™ G-25) of equilibration buffer to completely remove the storage solution. - For PD MiniTrap™ G-25: Add 100 to 500 µL of sample to the column. For sample volumes lower than 500 µL, add equilibration buffer to adjust the volume up to 500 µL after the sample has entered the packed bed completely.
- For PD MidiTrap™ G-25: Add 0.5 to 1.0 mL of sample to the column. For sample volumes lower than 1.0 mL, add equilibration buffer to adjust the volume up to 1.0 mL after the sample has entered the packed bed completely.
- Allow the sample and equilibration buffer to enter the packed bed completely. Discard the flowthrough.
- Place a test tube for sample collection under the column and elute with 1 mL (PD MiniTrap™ G-25) or 1.5 mL (PD MidiTrap™ G-25) buffer. Collect the desalted sample.
Recovery is dependent on type of protein. Typically, recovery is in the range of 70% to 90%. Concentration of the sample (e.g., using a Vivaspin® sample concentrator) can improve recovery. Recovery and desalting capacity are higher when using gravity flow compared with centrifugation. A typical result for desalting of a protein with PD MiniTrap™ G-25 is shown in Figure 11.7.
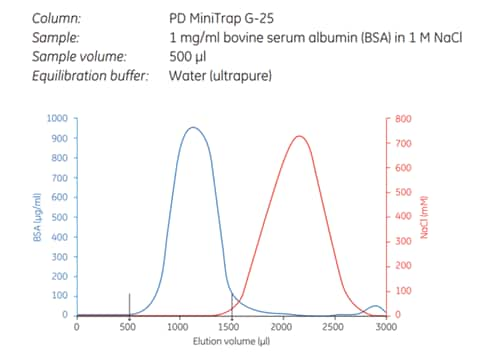
Figure 11.7.Removal of NaCl from BSA using the gravity protocol. The protein recovery was 95%.
Centrifugation protocol
Buffer
Equilibration buffer: Buffer of choice
Desalting procedure
- Remove the top cap and pour off the column storage solution.
- Remove the top filter using forceps. Remove the bottom cap.
- Place the column into a 15 mL (PD MiniTrap™ G-25) or 50 mL (PD MidiTrap™ G-25) collection tube and connect the supplied column adapter to the top of the tube.
- Fill the column with equilibration buffer and allow the equilibration buffer to enter the packed bed completely. Repeat and discard the flowthrough.
- Fill the column with equilibration buffer again and centrifuge at 1000 x g for 2 min and discard the flowthrough.
To ensure optimal results, it is critical to equilibrate the column with a total of 8 mL (PD MiniTrap™ G-25) or 15 mL (PD MidiTrap™ G-25) of equilibration buffer (steps 4 and 5) to completely remove the storage solution. - For PD MiniTrap™ G-25: Add 200 to 500 µL of sample slowly to the middle of the packed bed. For PD MidiTrap™ G-25: Add 0.75 to 1.0 mL of sample slowly to the middle of the packed bed.
- Place the column into a new 15 mL (PD MiniTrap™ G-25) or 50 mL (PD MidiTrap™ G-25) collection tube.
- Elute by centrifugation 1000 × g for 2 min and collect the eluate.
Recovery is dependent on type of protein. Typically, recovery is in the range of 70% to 90%. Concentration of the sample (e.g., using a Vivaspin® sample concentrator) can improve recovery. Recovery and desalting capacity are higher using gravity flow compared with centrifugation.
For desalting larger sample volumes, use HiTrap® and HiPrep™ columns; see Table 11.1.
PD-10 Desalting columns
PD-10 Desalting columns are designed for convenient desalting and buffer exchange of 1.0 to 2.5 mL volume of protein sample. The columns are prepacked with Sephadex G-25 Medium, an SEC medium that allows effective removal of low molecular weight substances from proteins with Mr > 5000. These columns provide an excellent alternative to PD MidiTrap™ G-25 columns because of the increased sample volume capacity.
For increased flexibility, the product has two alternative application protocols, using either gravity or centrifugation. The gravity protocol allows simple cleanup of multiple samples in parallel without the need for a purification system. Using the centrifugation protocol, samples are run in a standard centrifuge with minimal dilution of the eluted sample.
Each pack of PD-10 Desalting columns contains 30 prepacked columns. To simplify the use of PD-10 Desalting columns with the gravity protocol, LabMate PD-10 Buffer Reservoir may be used. Using the buffer reservoir, wash and equilibration buffers can be applied in one step.
A typical separation is shown in Figure 11.8.
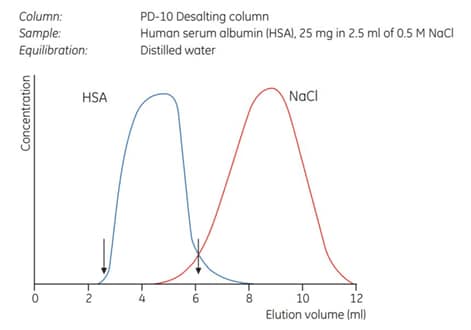
Figure 11.8.Removal of NaCl from albumin solution. A PD-10 Desalting column was equilibrated with distilled water. A total of 23.8 mg of albumin was recovered in 3.5 mL of eluent corresponding to a yield of 95.3% (between arrows).
Gravity Protocol
Buffer
Equilibration buffer: Buffer of choice
Desalting procedure
- Cut off bottom tip, remove top cap, and pour off excess liquid.
- If available, mount the LabMate Buffer Reservoir on top of the PD-10 Desalting column and place the columns in the PD-10 Desalting LabMate.
- Equilibrate the column with approximately 25 mL of buffer. Discard the flowthrough (use the plastic tray to collect flowthrough).
To ensure optimal results, it is critical to equilibrate the column with a total of 25 mL of equilibration buffer to completely remove the storage solution. - Add sample of a total volume of 2.5 mL. If the sample is less than 2.5 mL, add buffer until the total volume of 2.5 mL is achieved. Discard the flowthrough.
- Elute with 3.5 mL of buffer and collect the flowthrough.
Recovery is dependent on type of protein. Typically, recovery is in the range of 70% to 90%. Concentration of the sample (e.g., using a Vivaspin® sample concentrator) can improve recovery. Recovery and desalting capacity are higher using gravity flow compared with centrifugation.
For desalting larger sample volumes, use HiTrap® and HiPrep™ columns; see Table 11.1.
Centrifugation protocol
Buffer
Equilibration buffer: Buffer of choice
Desalting procedure
- Remove the top cap and pour off the column storage solution.
- Remove the top filter using forceps. Remove the bottom cap.
- Place the PD-10 Desalting column into a 50 mL collection tube and connect the supplied column adapter to the top of the tube.
- Fill the column with equilibration buffer and allow the equilibration buffer to enter the packed bed completely. Repeat three times, discarding the flowthrough each time.
- Fill the column with equilibration buffer again and centrifuge at 1000 x g for 2 min and discard the flowthrough.
- To ensure optimal results, it is critical to equilibrate the column with a total of 25 mL of equilibration buffer (steps 4 and 5) to completely remove the storage solution.
- Add 1.75 to 2.5 mL of sample slowly to the middle of the packed bed.
- Place the PD-10 Desalting column into a new 50 mL collection tube.
- Elute by centrifugation 1000 × g for 2 min and collect the eluate.
Recovery is dependent on type of protein. Typically, recovery is in the range of 70% to 90%. Concentration of the sample (e.g., using a Vivaspin® sample concentrator) can improve recovery. Recovery and desalting capacity are higher using gravity flow compared with centrifugation.
For desalting larger sample volumes, use HiTrap® and HiPrep™ columns; see Table 11.1.
PD MiniTrap™ G-10 and PD MidiTrap™ G-10
PD MiniTrap™ G-10 and PD MidiTrap™ G-10 are designed for convenient desalting and buffer exchange of 100 to 300 µL (PD MiniTrap™ G-10) or 0.4 to 1.0 mL (PD MidiTrap™ G-10) volume of protein sample (Figure 11.9). The columns are prepacked with Sephadex G-10 Medium, an SEC medium that allows effective removal of low molecular weight substances from proteins with Mr > 700. Each pack of PD MiniTrap™ G-10 and PD MidiTrap™ G-10 contains 50 prepacked columns.

Figure 11.9.PD MidiTrap™ G-10 (left) and PD MiniTrap™ G-10 (right) columns are prepacked with Sephadex G-10.
Gravity protocol
Buffer
Equilibration buffer: Buffer of choice
Desalting procedure
- Resuspend the medium by shaking the column. Allow the medium to settle. Remove the top and bottom caps, and allow the storage solution to flow out.
- Fill the column with equilibration buffer and allow the equilibration buffer to enter the packed bed completely. Repeat twice and discard the flowthrough.
- To ensure optimal results, it is critical to equilibrate the column with 8 mL (PD MiniTrap™ G-10) or 16 mL (PD MidiTrap™ G-10) of equilibration buffer to completely remove the storage solution.
- For PD MiniTrap™ G-10: Add a maximum of 300 µL of sample to the column. Add equilibration buffer to adjust the volume up to 700 µL after the sample has entered the packed bed completely.
- For PD MidiTrap™ G-10: Add a maximum of 1.0 mL of sample to the column. Add equilibration buffer to adjust the volume up to
1.7 mL after the sample has entered the packed bed completely. - Allow the sample and equilibration buffer to enter the packed bed completely. Discard the flowthrough.
- Place a test tube for sample collection under the column and elute with 0.5 mL (PD MiniTrap™ G-10) or 1.2 mL
(PD MidiTrap™ G-10) of buffer. Collect the desalted sample.
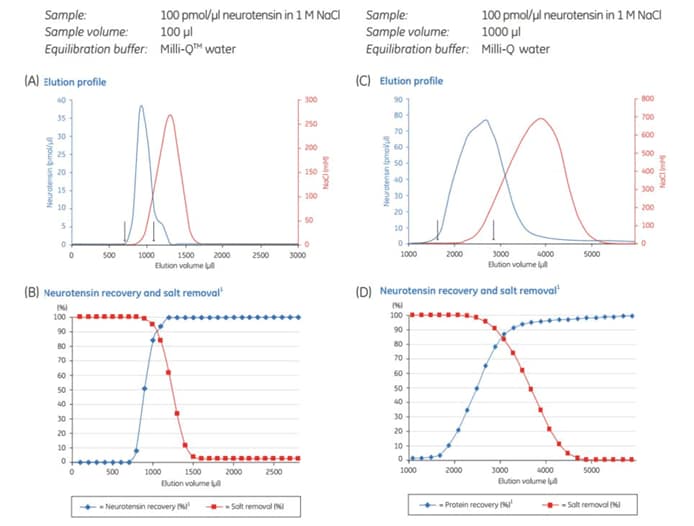
Figure 11.10.Removal of NaCl from a neurotensin (a 13 amino acid neuropeptide) solution. The neurotensin recovery was 81% and the desalting capacity was 84% (between arrows) for the PD MiniTrap™ G-10 (A & B). For the PD MidiTrap™ G-10 (C & D) neurotensin recovery was 79% and desalting capacity was 91% (between arrows). The recovery was calculated by measuring the absorbance at 215 nm, and the desalting capacity was measured by conductivity. Graphs B & D show neurotensin recovery and salt removal versus the total elution volume on the column for PD MiniTrap™ G-10 and PD MidiTrap™ G-10, respectively.
HiTrap® Desalting Columns

Figure 11.11.HiTrap® Desalting column allows efficient, easy-to-perform group separations with a syringe, pump, or chromatography system
HiTrap® Desalting is a 5 mL column (Figure 11.11) packed with the SEC medium Sephadex G-25 Superfine, which is based on cross-linked dextran beads. The fractionation range for globular proteins is between Mr 1000 and 5000, with an exclusion limit of approximately Mr 5000. This ensures group separations of proteins/peptides larger than Mr 5000 from molecules with a molecular weight less than Mr 1000.
HiTrap® Desalting can be used with aqueous solutions in the pH range 2 to 13. The prepacked medium is stable in all commonly used buffers, solutions of urea (8 M), Gua-HCl (6 M), and all nonionic and ionic detergents. Lower alcohols (methanol, ethanol, propanol) can be used in the buffer or the sample, but we recommend that the concentration be kept below 25% v/v. Prolonged exposure (hours) to pH below 2 or above 13, or to oxidizing agents, should be avoided.
The recommended range of sample volumes is 0.1 to 1.5 mL when complete removal of low molecular weight components is desired. The separation is not affected by the flow rate, in the range of 1 to 10 mL/min. The maximum recommended flow rate is 15 mL/min. Separations are easily performed with a syringe, pump, or chromatography system. Up to three columns can be connected in series, allowing larger sample volumes to be handled. To avoid cross-contamination, use the column only with the same type of sample.
Figure 11.12 shows a typical desalting and buffer exchange separation achieved using HiTrap® Desalting and monitored by following changes in UV absorption and conductivity.
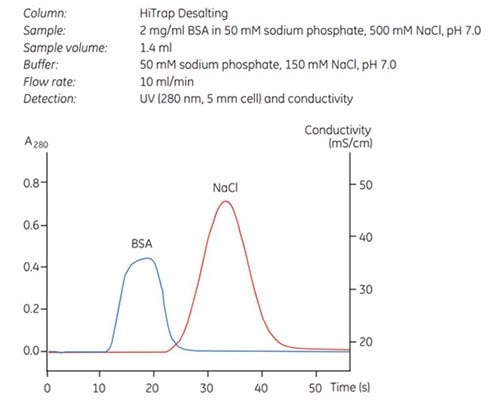
Figure 11.12.Highly efficient desalting in 30 s using HiTrap® Desalting.
Buffer
Equilibration buffer: Buffer of choice
Column Equilibration
- Fill the syringe or pump tubing with buffer. Remove the stopper. To avoid introducing air into the column, connect the column “drop to drop” to either the syringe (via the connector) or to the pump tubing.
- Remove the snap-off end at the column outlet.
- Wash the column with 25 mL of buffer at 5 mL/min to completely remove the storage buffer, which contains 20% ethanol1. If air is trapped in the column, wash with degassed buffer until the air disappears. Air introduced into the column by accident during sample application does not influence the separation.
1 5 mL/min corresponds to approximately 120 drops/min when using a HiTrap® 5 mL column.
Manual Desalting Using a Syringe
- To operate the column with a syringe, connect the syringe to the column using the supplied connector.
- Equilibrate the column; see previous page, Column equilibration.
- Apply the sample using a 2 to 5 mL syringe at a flow rate between 1 and 10 mL/min1. Discard the liquid eluted from the column. If the sample volume is less than 1.5 mL, change to buffer and proceed with the injection until a total of 1.5 mL has been eluted. Discard the eluted liquid.
- Elute the protein with the appropriate volume selected from Table 11.2. Collect the desalted protein.
1 5 mL/min corresponds to approximately 120 drops/min when using a HiTrap® 5 mL column.
The maximum recommended sample volume when using one HiTrap® Desalting 5 mL column is 1.5 mL. See Table 11.2 for information on application of smaller sample volumes.
The void volume of the column is 1.5 mL. High molecular weight components elute between 1.5 and 4.5 mL, depending on the sample volume. Low molecular weight components start to elute after 3.5 mL.
Certain types of molecules, such as small heterocyclic or homocyclic aromatic compounds (purines, pyrimidines, dyes) can interact with Sephadex and are therefore eluted later than expected. Larger sample volumes can be used in these cases, but the separation has to be optimized for each type of contaminating compound.
Desalting Using a Pump
- Equilibrate the column: see Column equilibration above.
- Apply up to 1.5 mL of sample. Monitor the effluent from the column with a UV monitor and/or a conductivity monitor. Keep the flow rate in range 1 to 10 mL/min. Collect fractions.
- Elute the column with approximately 10 mL of buffer before applying the next sample. Collect fractions.
Scaling up desalting from HiTrap® to HiPrep™ Desalting
For separation of sample volumes larger than 1.5 mL, or to increase the resolution between high and low molecular weight components, up to three HiTrap® Desalting columns can easily be connected in series. For syringe operations, the volumes suggested in Table 11.2 should be increased proportionally and the recommended flow rate maintained.
The dilution of the sample is dependent on the sample volume and the number of columns used in series. Lower dilution factors than those proposed in Table 11.2 can be obtained, but the elution volumes have to be optimized for each combination of sample volume and number of columns in series. The back pressure for each column is approximately 0.25 bar at 10 mL/min.
HiPrep™ 26/10 Desalting is packed with Sephadex G-25 Fine. It provides group separation of high (Mr > 5000) from low molecular weight substances (Mr < 1000), allowing reliable and reproducible desalting and buffer exchange with sample sizes of 15 mL per column. Two to four columns can be used in series (Table 11.1) for sample volumes of 30 to 60 mL.
Protein Sample Concentration
Figure 11.13.Vivaspin® sample concentrators provide up to 30-fold concentration of the sample with recovery of the target molecule typically exceeding 95%.
Vivaspin® sample concentrators are designed for fast, nondenaturing concentration of biological samples by membrane ultrafiltration. Up to 30-fold concentration of the sample can be achieved with recovery of the target molecule typically exceeding 95%. The entire process is performed in a single tube with an upper compartment containing sample and lower compartment separated by a semipermeable membrane with a molecular weight cutoff (MWCO) selected by the user. Centrifugation is applied to force solvent through the membrane, leaving a more concentrated sample in the upper chamber.
Vivaspin® sample concentrators can be used with sample volumes from 100 µL to 20 mL, with a range of MCWO values from Mr 3000 to 100 000. All products are available with MCWO values of 3000, 5000, 10 000, 30 000, 50 000, and 100 000 (Table 11.3).
- Select the most appropriate membrane cut-off for your sample. For maximum recovery select a MWCO at least 50% smaller than the molecular size of the species of interest.
- Fill concentrator with up to the maximum volumes shown in Appendix 12 (Tables for Vivaspin® sample concentrators), Table A12.1.
(Ensure lid is fully seated.) - Insert the assembled concentrator into centrifuge.
Note: If using a fixed angle rotor, angle concentrator so that the printed window faces upward/outward. - Set centrifugation speed as recommended in Appendix 12 (Tables for Vivaspin® sample concentrators), Table A12.2, taking care not to exceed the maximum g-force indicated.
- Set centrifugation time (concentration time) after consulting Appendix 12 (Tables for Vivaspin® sample concentrators), Table A12.3 to Table A12.6 for typical recoveries for various combinations of proteins, Vivaspin® products, and filters.
- Concentrate samples by using centrifugation speed and time set in steps 4 and 5.
- Remove assembly and recover sample from the bottom of the concentrate pocket with a pipette. The filtrate tube can be sealed for storage.
To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?