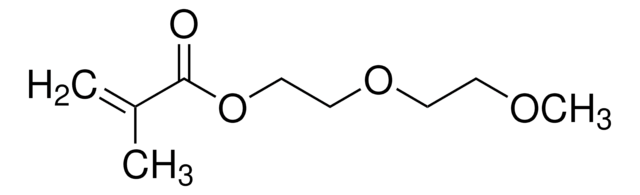
推荐产品
形式
liquid
分子量
average Mn 360
包含
500-800 ppm MEHQ as inhibitor
反应适用性
reagent type: cross-linking reagent
reaction type: Polymerization Reactions
折射率
n20/D 1.464
密度
1.105 g/mL at 25 °C
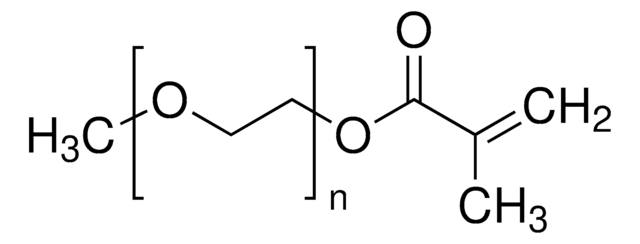
Ω端
hydroxyl
α端
methacrylate
聚合物结构设计
shape: linear
functionality: heterobifunctional
InChI
1S/C6H10O3/c1-5(2)6(8)9-4-3-7/h7H,1,3-4H2,2H3
InChI key
WOBHKFSMXKNTIM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
正在寻找类似产品? Visit 产品对比指南
一般描述
应用
- 可降解微球,采用悬浮聚合工艺。PEGMA 的两亲性允许在水悬浮过程中通过直接油进行聚合。
- 用于有效去除水中重金属的聚合螯合微珠。
外形
警示用语:
Warning
危险声明
危险分类
Skin Irrit. 2
储存分类代码
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 3
闪点(°F)
235.4 °F - closed cup
闪点(°C)
113 °C - closed cup
个人防护装备
Eyeshields, Gloves, type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter
分析证书(COA)
输入产品批号来搜索 分析证书(COA) 。批号可以在产品标签上"批“ (Lot或Batch)字后找到。
已有该产品?
为方便起见,与您过往购买产品相关的文件已保存在文档库中。
难以找到您所需的产品或批次号码?
如何查找产品货号
在网站页面上,产品编号会附带包装尺寸/数量一起显示(例如:T1503-25G)。请确保 在“产品编号”字段中仅输入产品编号 (示例: T1503).
示例
其它示例:
705578-5MG-PW
PL860-CGA/SHF-1EA
MMYOMAG-74K-13
1000309185
输入内容 1.000309185)
遇到问题?欢迎随时联系我们技术服务 寻求帮助
如何查找COA批号
批号可以在产品标签上"批“ (Lot或Batch)字后面找到。
Aldrich 产品
如果您查询到的批号为 TO09019TO 等,请输入去除前两位字母的批号:09019TO。
如果您查询到的批号含有填充代码(例如05427ES-021),请输入去除填充代码-021的批号:05427ES。
如果您查询到的批号含有填充代码(例如 STBB0728K9),请输入去除填充代码K9的批号:STBB0728。
未找到您寻找的产品?
部分情况下,可能未在线提供COA。如果搜索不到COA,可在线索取。
商品
Progress in biotechnology fields such as tissue engineering and drug delivery is accompanied by an increasing demand for diverse functional biomaterials. One class of biomaterials that has been the subject of intense research interest is hydrogels, because they closely mimic the natural environment of cells, both chemically and physically and therefore can be used as support to grow cells. This article specifically discusses poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) hydrogels, which are good for biological applications because they do not generally elicit an immune response. PEGs offer a readily available, easy to modify polymer for widespread use in hydrogel fabrication, including 2D and 3D scaffold for tissue culture. The degradable linkages also enable a variety of applications for release of therapeutic agents.
Devising biomaterial scaffolds that are capable of recapitulating critical aspects of the complex extracellular nature of living tissues in a threedimensional (3D) fashion is a challenging requirement in the field of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.
Devising biomaterial scaffolds that are capable of recapitulating critical aspects of the complex extracellular nature of living tissues in a threedimensional (3D) fashion is a challenging requirement in the field of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门