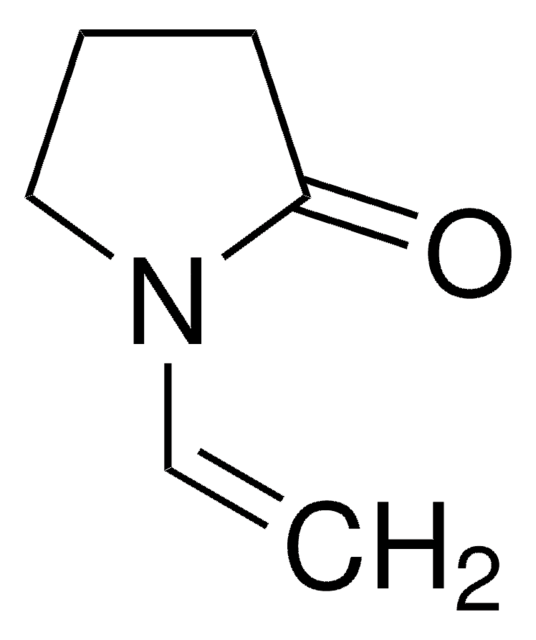
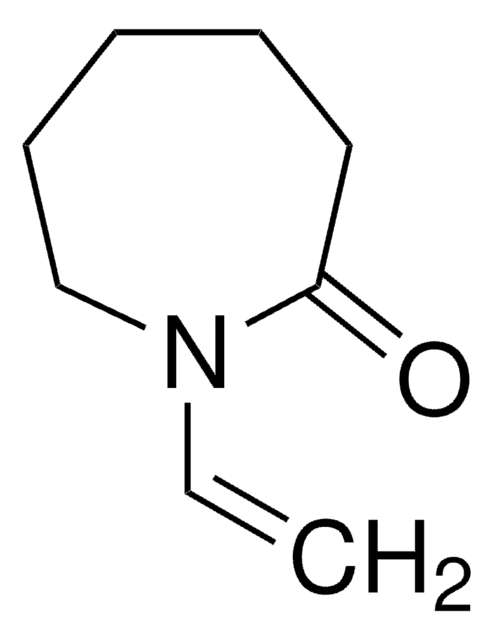
推荐产品
蒸汽密度
3.8 (vs air)
质量水平
蒸汽压
0.1 mmHg ( 24 °C)
检测方案
≥99%
自燃温度
685 °F
包含
sodium hydroxide as inhibitor
100 ppm sodium hydroxide as inhibitor (added to bulk material)
expl. lim.
10 %
折射率
n20/D 1.512 (lit.)
bp
92-95 °C/11 mmHg (lit.)
密度
1.04 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
储存温度
2-8°C
SMILES字符串
C=CN1CCCC1=O
InChI
1S/C6H9NO/c1-2-7-5-3-4-6(7)8/h2H,1,3-5H2
InChI key
WHNWPMSKXPGLAX-UHFFFAOYSA-N
正在寻找类似产品? Visit 产品对比指南
一般描述
应用
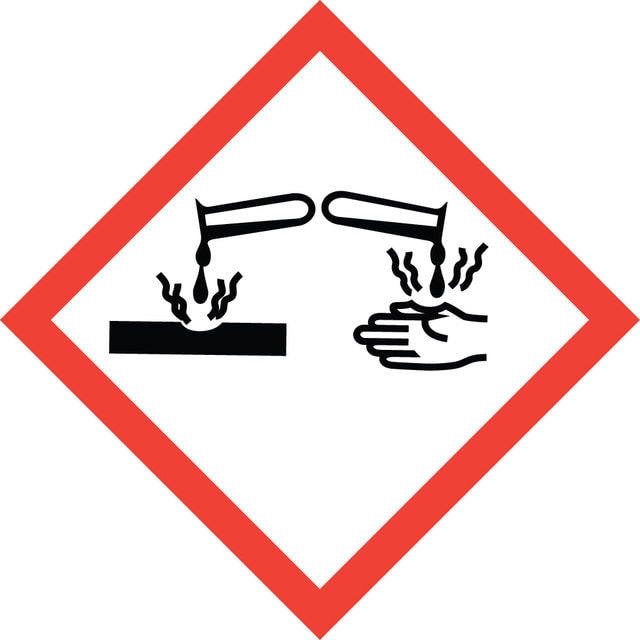
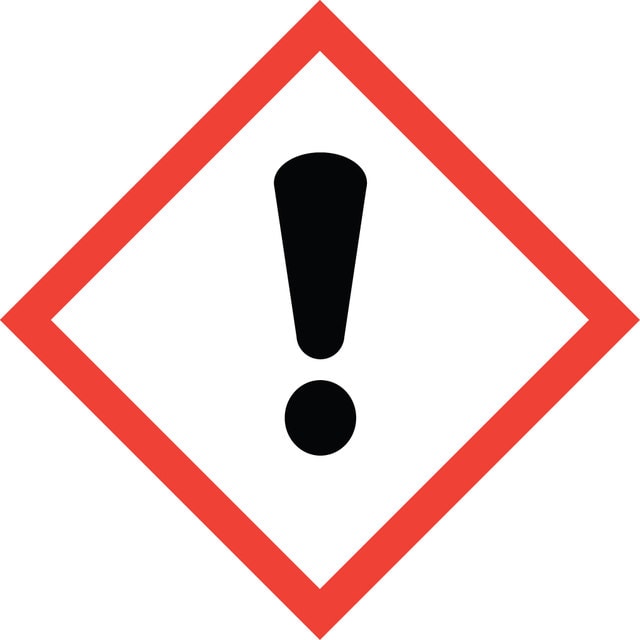
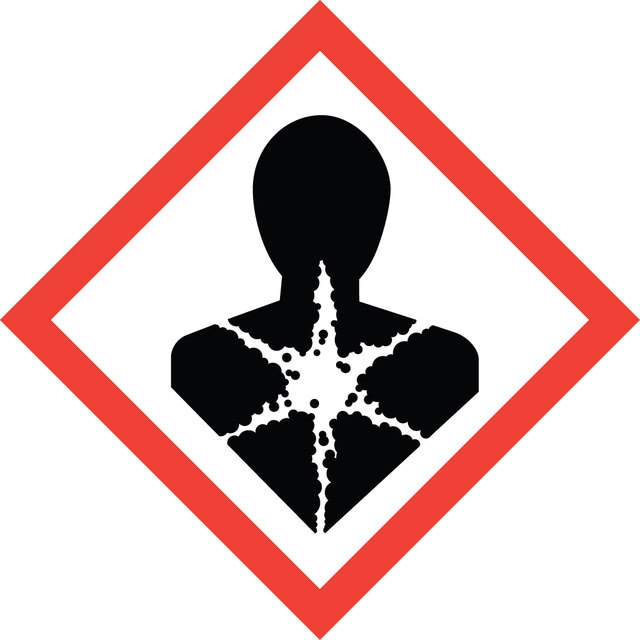
警示用语:
Danger
危险分类
Acute Tox. 4 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Carc. 2 - Eye Dam. 1 - STOT RE 2 - STOT SE 3
靶器官
Respiratory system
储存分类代码
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 1
闪点(°F)
203.0 °F - closed cup
闪点(°C)
95 °C - closed cup
个人防护装备
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter
分析证书(COA)
输入产品批号来搜索 分析证书(COA) 。批号可以在产品标签上"批“ (Lot或Batch)字后找到。
已有该产品?
为方便起见,与您过往购买产品相关的文件已保存在文档库中。
难以找到您所需的产品或批次号码?
如何查找产品货号
在网站页面上,产品编号会附带包装尺寸/数量一起显示(例如:T1503-25G)。请确保 在“产品编号”字段中仅输入产品编号 (示例: T1503).
示例
其它示例:
705578-5MG-PW
PL860-CGA/SHF-1EA
MMYOMAG-74K-13
1000309185
输入内容 1.000309185)
遇到问题?欢迎随时联系我们技术服务 寻求帮助
如何查找COA批号
批号可以在产品标签上"批“ (Lot或Batch)字后面找到。
Aldrich 产品
如果您查询到的批号为 TO09019TO 等,请输入去除前两位字母的批号:09019TO。
如果您查询到的批号含有填充代码(例如05427ES-021),请输入去除填充代码-021的批号:05427ES。
如果您查询到的批号含有填充代码(例如 STBB0728K9),请输入去除填充代码K9的批号:STBB0728。
未找到您寻找的产品?
部分情况下,可能未在线提供COA。如果搜索不到COA,可在线索取。
商品
The manufacture of monomers for use in ophthalmic applications is driven by the need for higher purity, improved reliability of manufacturing supply, but ultimately by the need for the increased comfort, convenience, and safety of contact lens wearers. Daily wear contact lenses have the potential to fill this need for many customers; however, their widespread use is constrained by higher costs compared to weekly- or monthly-based lenses. New approaches that improve cost structure and result in higher quality raw materials are needed to help make contact lenses more affordable and accelerate growth of the contact lens market.
The manufacture of monomers for use in ophthalmic applications is driven by the need for higher purity, improved reliability of manufacturing supply, but ultimately by the need for the increased comfort, convenience, and safety of contact lens wearers. Daily wear contact lenses have the potential to fill this need for many customers; however, their widespread use is constrained by higher costs compared to weekly- or monthly-based lenses. New approaches that improve cost structure and result in higher quality raw materials are needed to help make contact lenses more affordable and accelerate growth of the contact lens market.
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门