CRISPR Engineered MDCKII Cells Without Canine P-glycoprotein
CRISPR Transporter Knockout Cells
Madin-Darby Canine Kidney (MDCK) cells are one of the most widely used cell lines for a variety of research applications, including drug permeability and transporter studies. One of the main drawbacks of using MDCK cells is high expression of the transporters of nonhuman origin, of which canine P-glycoprotein (cP-gp) significantly interferes with permeability and transporter studies.
Using Clustered Regularly-Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR) genome editing technology, our scientists have engineered a cP-gp knock out MDCKII cell line, which has no cP-gp activity, and is a more predictive model for drug transporter and permeability studies.
A transfection of either human BCRP (hBCRP) or human P-glycoprotein (hPg-p) has been made within the MDCKII cP-gp knockout clone. With the correct apical polarity these models are useful in drug transporter studies.
Our Transporter Knockout cells can be used in cell-based assays for accurate identification of drug-transporter interactions. These cells deliver robust efflux activity, stable transporter knockout, reproducible results, save time and costs, and provide assay flexibility.
Benefits of CRISPR Knockout Cells
- Permanent knockout of cP-gp drug transporter eliminates background activity
- Explicitly identify transporters(s) responsible for active efflux of substrates
- Insert directly into your drug transporter testing workflow
- No need to run compounds through the wild type MDCKII after running compounds through the transfected cell line
cP-gp Knockout hP-gp transfected MDCKII Cell Lines
Human P-gp transfected MDCKII cell lines have the added benefit of having the cainine P-gp gene inactivated on both alleles through the disruption of gene expression using CRISPR gene editing techniques. Digoxin, Erythromycin and Quinidine are P-gp substrates with examples of efflux ratios ≥2. In contrast, Triprolidine is not a P-gp substrate.
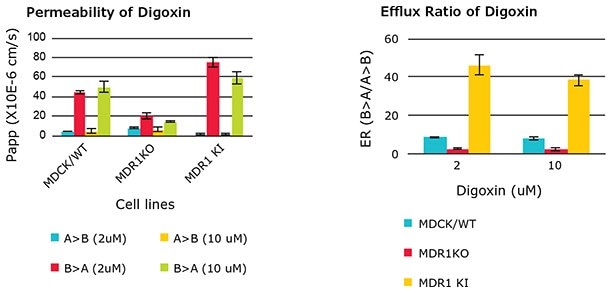
Permeability (Papp) and efflux ratio (ER) of MDR1 substrate digoxin in wild type (WT), cMDR1 knockout (KO) and hMDR1 transduced (KI) MDCKII cells. Papp (B to A) of digoxin in cMDR1 KO cells was reduced significantly and ER decreased to less than 2, confirming the loss function of MDR1 in cMDR1 KO cells. Conversely, Papp (B to A) from hMDR1 KI cells increased dramatically and ER returned to a value greater than 30, indicating presence of human MDR1 function in hMDR1 KI cells.
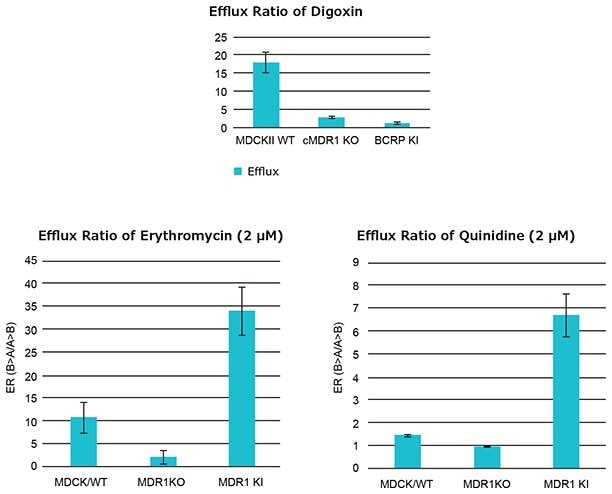
Efflux ratio (ER) of additional MDR1 substrates, erythromycin and quinidine. ER values for both compounds were reduced to less than 2 in the cMDR1 KO cells compared to WT cells. Alternatively, ER increased in the hMDR1 KI cells compared to cMDR1 KO cells.

Permeability (Papp) and efflux ratio (ER) of the non-MDR1 substrate triprolidine. Papp values (both A to B and B to A) were similar in WT, cMDR1 KO and hMDR KI cell lines. ER values were around 1 in all cell lines. The A to B Papp values demonstrated that the compound belongs to the high permeable class, which is consistent with literature reports. These data also indicated that the MDR1 modifications did not effect the permeability of non-MDR1 substrates.
cP-gp Knockout hBCRP transfected MDCKII Cell Lines
Human Breast Cancer Resistant Protein (BCRP) transfected MDCKII cell lines have the added benefit of having the cainine P-gp gene inactivated on both alleles through the disruption of gene expression using CRISPR gene editing techniques. Topotecan, Teriflunomide and SN-38 are hBCRP substrates with examples of efflux ratios ≥ 2.
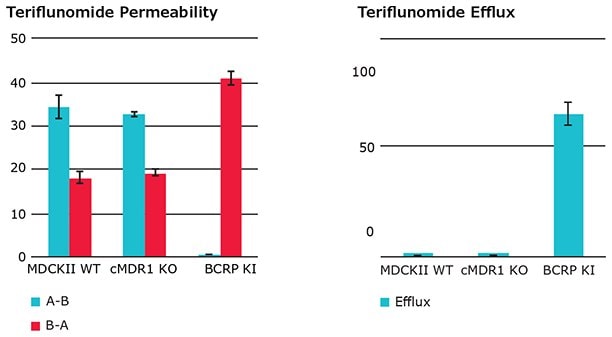
Permeability (Papp) and efflux ratio (ER) of hBCRP substrate Teriflunomide in wild type (WT), cMDR1 knockout (KO) and hBCRP transduced (KI) MDCKII cells. Efflux ratios for Teriflunomide were less than 2 for wt MDCKII. Efflux ratios where substantially greater than 2 for the cMDR1 KO hBCRP transfected cell line.
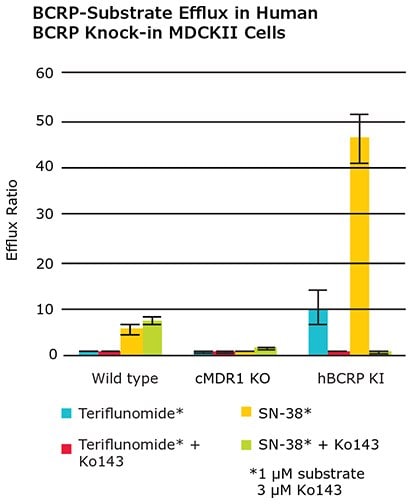
Efflux ratio (ER) of BCRP substrates Teriflunomide & SN-38, ER values for both compounds were reduced to less than 2 in the cMDR1 KO cells WT cells. Alternatively, ER efflux ratios substantially increased for both Teriflunomide & SN-3 when exposed to the hBCRP tranfected cell line. When BCRP inhibitor, Ko143, was added in tandem with substrates Teriflunomide and SN-38, the hBCRP transfected cell line showed efflux ratios below 2.
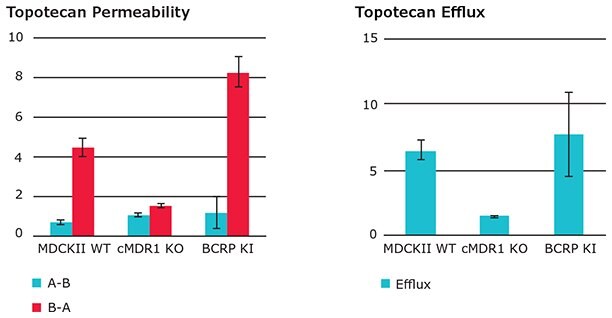
Permeability (Papp) and efflux ratio (ER) of hBCRP substrate Topotecan in wild type (WT), cMDR1 knockout (KO) and hBCRP transduced (KI) MDCKII cells. Efflux ratios for Topotecan were less than 2 for wt MDCKII & cMDR1 knockout (KO). Efflux ratios where greater than 2 for the cMDR1 KO hBCRP transfected cell line.

MDCKII subclone was originally isolated by Daniel Louvard, Institut Curie, Paris France.
References
To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?